Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nagakubo, Azusa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-027, 146 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been applied as a method to quickly and extensively measure the distribution of radiation. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has continuously conducted ARM via manned helicopter around FDNPS. In this report, we summarize the results of the ARM around FDNPS in the fiscal year 2022, evaluate the changes of ambient dose rates and other parameters based on the comparison to the past ARM results, and discuss the causes of such changes. In order to contribute to improve the accuracy of ambient dose rate conversion, we analyzed the ARM data taking into account undulating topography, and evaluated the effect of this method. Furthermore, the effect of radon progenies in the air on the ARM was evaluated by applying the discrimination method to the measurement results.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-026, 161 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been utilized as a method to quickly and extensively measure radiation distribution surrounding FDNPS. In order to utilize ARM and to promptly provide the results during a nuclear emergency, information on background radiation levels, topographical features, and controlled airspace surrounding nationwide nuclear facilities have been prepared in advance. In the fiscal year 2022, we conducted ARM around the Mihama Nuclear Power Station of Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO), the Tsuruga Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC), and the Ikata Power Station of Shikoku Electric Power Company (YONDEN), and prepared information on background radiation doses and controlled airspace. In addition, we have developed an aerial radiation detection system via unmanned airplane, which is expected to be an alternative to ARM, during a nuclear emergency. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified.
Fukahori, Tokio
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (137), p.1 - 10, 2024/02
At the request of the EC/Joint Research Center, the author attended on an EU-sponsored side event "Providing the best nuclear data for tomorrow's nuclear solutions: challenges and opportunities" held simultaneously at the IAEA 67th General Conference as a panelist. Presented were the prospects for nuclear data activities in Japan and discussed the sustainability and revitalization of nuclear data activities. In addition, based on the roundtable discussion at this side event, the Nuclear Data Section held a meeting consisting mainly of panelists to consider future responses. In this article, I would like to report on the side event and subsequent follow-up meetings and discuss the background of these meetings.
Nagai, Takayuki; Hasegawa, Takehiko*
JAEA-Research 2023-008, 41 Pages, 2023/12
To reduce the risks posed by stored the high-level radioactive liquid waste (HAW), Tokai Vitrification Facility (TVF) is working to produce the HAW into vitrified bodies. With the aim of steady vitrification of HAW in TVF, the vitrification technology section has manufactured a new 3rd melter with an improved bottom structure and is working to verify the performance of this melter. In this study, solidified glass samples were taken from simulated vitrified bodies produced by flowing molten glass during the bottom drain-out test in the operation confirmation of the TVF 3rd melter. And the properties of the surface layer and fracture surface of the vitrified bodies were evaluated by using Raman spectroscopy, synchrotron radiation XAFS measurement, and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (LA ICP-AES) analysis. As a result of measuring the surface layer and fracture surface of the solidified samples produced on an actual scale, a slight difference was confirmed between the properties of the surface layer and those of the fracture surface. Since the chemical composition of these simulated vitrified bodies does not contain platinum group elements, it is expected that the glass structure of solidified glass samples is different from that of the actual vitrified body. However, this sample measuring was a valuable opportunity to evaluate samples produced by using the direct energized joule heating method. The properties of cullet used the operation confirmation of the TVF 3rd melter and the cullet of another production lot were measured and analyzed in the same manner under the measuring conditions of solidified glass samples. As a result, it was confirmed that cullet with different producing histories have different glass structures even with the same chemical composition, and that differences in glass structures remain in the glass samples after melting these cullet.
Tsubota, Yoichi; Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Suteau, C.*; Lallot, Y.*; Bouland, A.*; Roulet, D.*; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
In order to safely remove fuel debris from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), it is necessary to quantitatively evaluate radioactive airborne particulate generated by the cutting of nuclear fuel debris. We fabricated Uranium-bearing simulated fuel debris (SFD) with In/Ex-Vessel compositions and evaluated the physical and chemical properties of aerosols generated by heating the SFDs. Based on these results, we estimated the isotopic composition and radioactivity of aerosols produced when 1F-Unit2 fuel debris is laser cut, which is a typical example of a heating method. Plutonium, mainly  Pu,
Pu, Am, and
Am, and  Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and
Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and  Pu,
Pu,  Cs-Ba, and
Cs-Ba, and  Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Tsubota, Yoichi; Ikeda, Atsushi; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
Results of the URASOL project aimed at evaluating the generation and dispersion of radioactive aerosols during the cutting of fuel debris, a key issue in the decommissioning of the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), are presented in this report. Characterization of aerosols generated during heating and mechanical cutting of simulated fuel debris in terms of mass concentration, real-time number density, mass-based particle size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties is reported. In the heating tests, an increase in particle size with increasing temperature was observed, and in terms of particle number density, the case using depleted uranium simulated fuel debris had a smaller number density than the test using Hf-containing simulated fuel debris. In mechanical cleavage, the aerodynamic median mass diameter of the aerosol was almost the same for the radioactive and non-radioactive samples (about 3.7 4.4
4.4  m).
m).
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-009, 165 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2020 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
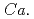 Methanoperedenaceae
MethanoperedenaceaeNishimura, Hiroki*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yohei*
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 15(3), p.197 - 205, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:59.23(Environmental Sciences)The family 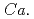 Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of
Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of 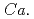 Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and
Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and  C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7
C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7 40.6 and 27.7
40.6 and 27.7 37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
Tada, Kenichi
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (135), p.1 - 10, 2023/06
This article summarizes presentations at the IAEA technical meeting on nuclear data processing. In this technical meeting, the current development status of nuclear data processing codes and comparisons of the processing results using these codes were presented.
Kokubu, Yoko; Fujita, Natsuko; Watanabe, Takahiro; Matsubara, Akihiro; Ishizaka, Chika; Miyake, Masayasu*; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Kato, Motohisa*; Ogawa, Yumi*; Ishii, Masahiro*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 539, p.68 - 72, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has an accelerator mass spectrometer (JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV). The spectrometer enabled us to use a multi-nuclide AMS of carbon-14 ( C), beryllium-10, aluminium-26 and iodine-129, and we have recently been proceeding test measurement of chlorine-36. In response to an increase of samples, we installed a state-of-the-art multi-nuclide AMS with a 300 kV Tandetron accelerator in 2020. Recently, we are driving the development of techniques of isobar separation in AMS and of sample preparation. Ion channeling is applied to remove isobaric interference and we are building a prototype AMS based on this technique for downsizing of AMS. The small sample graphitization for
C), beryllium-10, aluminium-26 and iodine-129, and we have recently been proceeding test measurement of chlorine-36. In response to an increase of samples, we installed a state-of-the-art multi-nuclide AMS with a 300 kV Tandetron accelerator in 2020. Recently, we are driving the development of techniques of isobar separation in AMS and of sample preparation. Ion channeling is applied to remove isobaric interference and we are building a prototype AMS based on this technique for downsizing of AMS. The small sample graphitization for  C has been attempted using an automated graphitization equipment equipped with an elemental analyzer.
C has been attempted using an automated graphitization equipment equipped with an elemental analyzer.
Shiwaku, Hideaki; Marushita, Motoharu*
JAEA-Research 2022-015, 39 Pages, 2023/05
We designed the hard X-ray undulator beamline BL22XU, which is dedicated to Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) at SPring-8 (now Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA)). BL22XU is used for XAFS (X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) analysis experiments to develop separation and extraction materials for radioactive waste treatment and to elucidate their chemical behavior, magnetic research experiments using a diffractometer, and experiments under extreme conditions using a high-pressure press and a diamond anvil cell. The available X-ray energy range was set from 3 to 70 keV. To design the optics of the beamline, the reflectivity of the mirrors, the diffraction width of the monochromatic crystal, and the absorptance of the Be window were calculated. In addition, ray tracing was performed to optimize the materials for optics, dimensions, and location. The delay time of the ADL (Acoustic Delay Line) was also examined to ensure the safety in the use of radioactive materials. The operation of BL22XU "JAEA Actinide Science I" has already started. By collaborating BL22XU and BL23SU "JAEA Actinide Science II," which uses a soft X-ray undulator as a light source, we solve the problems to promote nuclear sciences. Since the monochromator was upgraded in 2018-2019, initial planning and measured data are documented here again.
Abe, Tomohisa; Funaki, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Shiribiki, Natsu*; Sanada, Yukihisa
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-001, 38 Pages, 2023/05
In this study, commissioned by the Cabinet Office, we conducted a survey on radioactive materials in atmospheric dust in three municipalities (Futaba Town, Okuma Town, and Tomioka Town) in Fukushima Prefecture to contribute to the assessment of internal exposure in the Specified Reconstruction and Revitalization Base (SRRB). Air dust samplers were installed in the targeted municipalities to investigate the atmospheric  Cs concentrations and to evaluate internal exposure doses based on measured value. This report summarizes the results of measurements between 2018 and 2021. A database of information on internal exposure dose assessment results based on atmospheric radioactivity concentrations and actual measurements, and meteorological observation data was compiled.
Cs concentrations and to evaluate internal exposure doses based on measured value. This report summarizes the results of measurements between 2018 and 2021. A database of information on internal exposure dose assessment results based on atmospheric radioactivity concentrations and actual measurements, and meteorological observation data was compiled.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Hokama, Tomonori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-028, 127 Pages, 2023/02
A large amount of radioactive material was released by the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company, caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring via manned helicopter has been utilized to grasp rapidly and widely the distribution of the radioactive materials surrounding FDNPS. We prepare the data of background radiation dose, geomorphic characteristics and the controlled airspace surrounding nuclear facilities of the whole country in order to make effective use of the monitoring technique as a way of emergency radiation monitoring and supply the results during an accident of a facility. This report has summarized the knowledge noted above achieved by the aerial radiation monitoring around Ohi and Takahama nuclear power stations. In addition, the examination's progress aimed at introducing airborne radiation monitoring via an unmanned plane during a nuclear disaster and the technical issues are summarized in this report.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nagakubo, Azusa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Urabe, Yoshimi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-027, 148 Pages, 2023/02
By the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011, a large amount of radioactive material was released from the FDNPS. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring via manned helicopter has been conducted around FDNPS. The results of the airborne radiation monitoring and the evaluation for temporal change of dose rate in the fiscal 2021 were summarized in this report. Analysis considering topographical effects was applied to the result of the airborne monitoring to improve the accuracy of the conventional method. In addition, technique for discriminating gamma rays from the ground and those from the airborne Rn-progenies was also utilized to evaluate their effect on airborne radiation monitoring.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-061, 59 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research on radioactive aerosol control and decontamination at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station decommissioning" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop a safe laser decontamination system that simultaneously incorporates an advanced particle detection and characterization system together with aerosol dispersion control in collaboration with the UK researchers. By using the UK partner's fundamental studies related to aerosol and water interface interactions, various methods such as electro-chemical processing of water-mist particles and spray droplets will be applied for effective control of ultra-fine aerosol particle dispersions in a large containment volume.
Di Palma, A.; Adamo, P.*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Sakoda, Akihiro; Sato, Kazuhiko; Iijima, Kazuki
Chemosphere, 308, Part 1, p.136179_1 - 136179_13, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.8(Environmental Sciences)The present study shows the use of mosses transplanted in bags, called as moss bags, as biosensors of airborne radioactive dusts in the environment of the evacuated zone of Fukushima. A standardized protocol was applied and three moss species were used. Background sites of Okayama Prefecture were used for comparison. In the Fukushima area, the moss bags were able to accumulate radiocaesium in all exposure sites and periods, with Sphagnum palustre moss acting as the most performant moss. The radiocaesium activity concentrations dectected in mosses were in strong agreement with the Cs deposition levels and decontamination status of each exposure site. The accumulation of soil-derived radiocaesium by moss bags was supported by autoradiography and electron microscopy analyses. The linear dependency of Cs accumulation with the exposure time allowed a radiocaesium quantitative assessment.
Sun, Haomin; Leblois, Y.*; Gelain, T.*; Porcheron, E.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1356 - 1369, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In severe accident scenarios of PWR, containment spray can be employed to washout the aerosol of radioactive materials, retaining them in the containment. Therefore, it is crucial to correctly predict the washout efficiency for safety assessment. For a PWR, a high spray coverage ratio ( 84%-95%) is required. However, experimental studies on the washout with such a high coverage ratio in a large vessel are quite limited. To understand such a washout phenomenon for model development, aerosol washout experiments are performed in a large vessel with not only aerosol measurements but also spray droplet characterizations. The spray coverage ratios are experimentally confirmed to be compatible with a real PWR. The washout features are investigated in detail. The model in MELCOR is examined using the measured aerosol removal rate, showing the removal rate tendency against particle diameters being reproduced. Although a significant underestimation occurs for large particles, a satisfactory agreement is obtained for smaller ones (
84%-95%) is required. However, experimental studies on the washout with such a high coverage ratio in a large vessel are quite limited. To understand such a washout phenomenon for model development, aerosol washout experiments are performed in a large vessel with not only aerosol measurements but also spray droplet characterizations. The spray coverage ratios are experimentally confirmed to be compatible with a real PWR. The washout features are investigated in detail. The model in MELCOR is examined using the measured aerosol removal rate, showing the removal rate tendency against particle diameters being reproduced. Although a significant underestimation occurs for large particles, a satisfactory agreement is obtained for smaller ones ( 0.52
0.52  m in diameter) corresponding to the minimum removal rate and around.
m in diameter) corresponding to the minimum removal rate and around.
Porcheron, E.*; Leblois, Y.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Molina, D.*; Suteau, C.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Roulet, D.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
One of the important challenges for the decommissioning of the damaged reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is the fuel debris retrieval. The URASOL project, which is undertaken by a French consortium consisting of ONET Technologies, CEA, and IRSN for JAEA/CLADS, is dedicated to acquiring basic scientific data on the generation and characteristics of radioactive aerosols from the thermal or mechanical processing of fuel debris simulant. Heating process undertaken in the VITAE facility simulates some representative conditions of thermal cutting by LASER. For mechanical cutting, the core boring technique is implemented in the FUJISAN facility. Fuel debris simulants have been developed for inactive and active trials. The aerosols are characterized in terms of mass concentration, real time number concentration, mass size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties. The chemical characterization aims at identifying potential radioactive particles released and the associated size distribution, both of which are important information for assessing possible safety and radioprotection measures during the fuel debris retrieval operations at 1F.
Tazaki, Makiko; Kimura, Takashi; Shimizu, Ryo; Tamai, Hiroshi; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Suda, Kazunori
JAEA-Review 2022-020, 82 Pages, 2022/09
As part of the "Research on Factor Analysis and Technical Processes for Achieving Denuclearization" started in 2018, comprehensive survey of nuclear development and denuclearization of Iraq was conducted, together with analysis of the characteristics and lessons learned from the denuclearization. Iraq's clandestine nuclear weapon related activities were initially focused on plutonium production, but it then switched its focus on producing highly enriched uranium, and built various facilities, including electromagnetic isotope separation (EMIS) and centrifuge uranium enrichment facilities. Denuclearization of Iraq began with the defeat in the 1991 Gulf War, which forced Iraq to accept United Nations Security Council Resolution 687 (1991) that year. The Resolution set out a framework for destruction, removal, or rendering harmless of Iraq's weapons of mass destruction (WMD) programs. Within the framework, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), with the support and cooperation of the newly established United Nations Special Commission (UNSCOM), had verified Iraq's past nuclear activities and denuclearization. Characteristics of Iraq's denuclearization include that 1) Iraq had no choice but to accept denuclearization, 2) IAEA was empowered to implement detectable inspection measures and methods, which later came to fruition as the IAEA Safeguards Agreement Additional Protocol (AP), 3) economic sanctions for the purpose of promoting denuclearization of Iraq were not very successful, and 4) denuclearization of Iraq and subsequent Iraq war, together with collapse of the Hussein regime, has affected the denuclearization of Libya, North Korea and Iraq. Furthermore, the lessons learned from the denuclearization are 1) the need for universalization of AP, and necessities for 2) economic sanctions that are suitable for the original purposes without being abused, 3) the need for diplomatic efforts including denuclearization frameworks and measures with a clear roadmap
Tamai, Hiroshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(8), p.465 - 467, 2022/08
, 64(8), p.465 - 467, 2022/08
Though nuclear safety and nuclear security share the same goal of protecting the public and the environment from the harmful effects of ionizing radiation, their response actions may have differences, especially during transport, where protection could be vulnerable. The interface between them is a major issue. In December 2021, with the aim of complementarily strengthening nuclear safety and nuclear security in the transportation of radioactive materials IAEA published a related technical report and held an international conference. The outline of the technical report and the international conference is introduced.